US closes part of Texas border, begins flying Haitians home
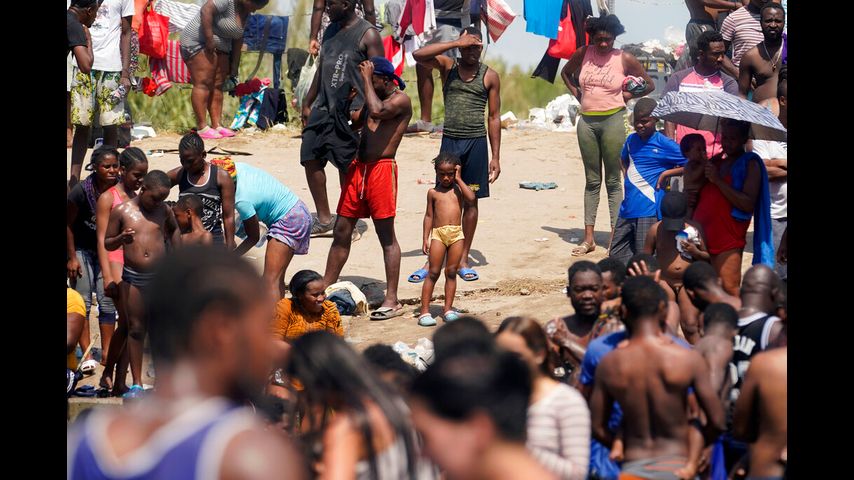


DEL RIO, Texas (AP) — The United States acted Sunday to stem the flow of migrants into Texas by blocking the Mexican border at an isolated town where thousands of Haitian refugees set up a camp, and American officials began flying some of the migrants back to their homeland.
About a dozen Texas Department of Public Safety vehicles lined up near the bridge and river where Haitians have been crossing from Ciudad Acuña, Mexico, into Del Rio, Texas, for almost three weeks.
The migrants initially found other ways to cross nearby until they were confronted by federal and state law enforcement. An Associated Press reporter saw Haitian immigrants still crossing the river into the U.S. about 1.5 miles (2.4 kilometers) east of the previous spot, but they were eventually stopped by Border Patrol agents on horseback and Texas law enforcement officials.
As they crossed, some Haitians carried boxes on their heads filled with food. Some removed their pants before getting into the river and carried them. Others were unconcerned about getting wet.
Agents yelled at the migrants who were crossing in the waist-deep river to get out of the water. The several hundred who had successfully crossed and were sitting along the river bank on the U.S. side were ordered to the Del Rio camp. "Go now," agents yelled.
Migrant Charlie Jean had crossed back into Ciudad Acuña from the camps to get food for his wife and three daughters, ages 2, 5 and 12. He was waiting on the Mexican side for a restaurant to bring him an order of rice.
"We need food for every day. I can go without, but my kids can't," said Jean, who had been living in Chile for five years before beginning the trek north to the U.S. It was unknown if he made it back across and to the camp.
Haitians have been migrating to the U.S. in large numbers from South America for several years, many having left their Caribbean nation after a devastating 2010 earthquake. After jobs dried up from the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro, many made the dangerous trek by foot, bus and car to the U.S. border, including through the infamous Darien Gap, a Panamanian jungle.
Some of the migrants at the Del Rio camp said the recent devastating earthquake in Haiti and the assassination of President Jovenel Moïse make them afraid to return to a country that seems more unstable than when they left.
"In Haiti, there is no security," said Fabricio Jean, a 38-year-old Haitian who arrived in Texas with his wife and two daughters. "The country is in a political crisis."
Border Patrol Chief Raul L. Ortiz said Sunday that 3,300 migrants have already been removed from the Del Rio camp to planes or detention centers, and he expects to have 3,000 of the approximately 12,600 remaining migrants moved within a day. The rest should be gone within the week, he said. The first three planes left San Antonio for Port-au-Prince on Sunday, with the first arriving in the afternoon.
"We are working around the clock to expeditiously move migrants out of the heat, elements and from underneath this bridge to our processing facilities in order to quickly process and remove individuals from the United States consistent with our laws and our policies," Ortiz said at news conference at the bridge.
The blockade and deportations marked a swift response to the sudden arrival of Haitians in Del Rio, a Texas city of about 35,000 people roughly 145 miles (230 kilometers) west of San Antonio. It sits on a relatively remote stretch of border that lacks capacity to hold and process such large numbers of people.
Meanwhile in Haiti, three flights landed at the Port-au-Prince airport, each carrying 145 people.
Families arriving on the first flight held children by the hand or carried them as they exited, and some of the 145 deportees covered their heads as they walked into a large bus parked next to the plane. Dozens lined up to receive a plate of rice, beans, chicken and plantains as they wondered where they would sleep and how they would make money to support their families.
All the deportees were given $100 and tested for COVID-19, though authorities were not planning to put them into quarantine, said Marie-Lourde Jean-Charles with the Office of National Migration.
Gary Monplaisir, 26, said his parents and sister live in Port-au-Prince, but he wasn't sure if he would stay with them because to reach their house he, his wife and their 5-year-old daughter would cross a gang-controlled area called Martissant where killings are routine.
"I'm scared," he said. "I don't have a plan."
He moved to Chile in 2017, just as he was about to earn an accounting degree, to work as a tow truck driver. He later paid for his wife and daughter to join him. They tried to reach the U.S. because he thought he could get a better-paying job and help his family in Haiti.
"We're always looking for better opportunities," he said.
Some migrants said they were planning to leave Haiti again as soon as possible. Valeria Ternission, 29, said she and her husband want to travel with their 4-year-old son back to Chile, where she worked as a bakery's cashier.
"I am truly worried, especially for the child," she said. "I can't do anything here."
One Haitian political leader questioned Sunday whether the nation could handle an influx of returning migrants and said the government should stop the repatriation.
"We have the situation in the south with the earthquake. The economy is a disaster, (and) there are no jobs," Election Minister Mathias Pierre said, adding that most Haitians can't satisfy basic needs. "The prime minister should negotiate with the U.S. government to stop those deportations in this moment of crises."
___
Lozano reported from Ciudad Acuña, Mexico, and Spagat reported from San Diego. Associated Press Writer Danica Coto in San Juan, Puerto Rico, also contributed to this report.
___
Follow AP's coverage of migration at https://apnews.com/hub/migration